Introduction
Welcome to the seventh installment of our Fortinet ZTNA series! In this guide, we explore the configuration of ZTNA tags and tagging rules—essential components that determine whether an endpoint is compliant or non-compliant when accessing data center (DC) resources. This step-by-step tutorial will walk you through setting up ZTNA tags, defining tagging rules, and understanding the available configuration options.
Zero-Trust Tagging Rules
Tagging rules are configured within FortiClient EMS (Endpoint Management System) and help classify endpoints based on compliance criteria.
Rule Types
Tagging Rules
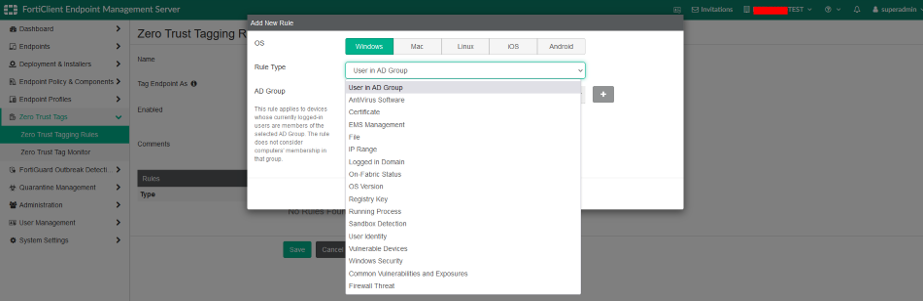
- Tagging rules vary depending on the operating system of the endpoint.
- The image above showcases some rule options available for Windows OS. (Fortinet continuously enhances telemetry to collect more endpoint data and update rules accordingly.)
- Each rule type provides different selection criteria. For example, when using an Active Directory (AD) Group rule, you must specify an AD group from the available domain groups. (Ensure your domain is properly configured under Endpoints to use this option.)
- Multiple conditions can be applied to any rule.
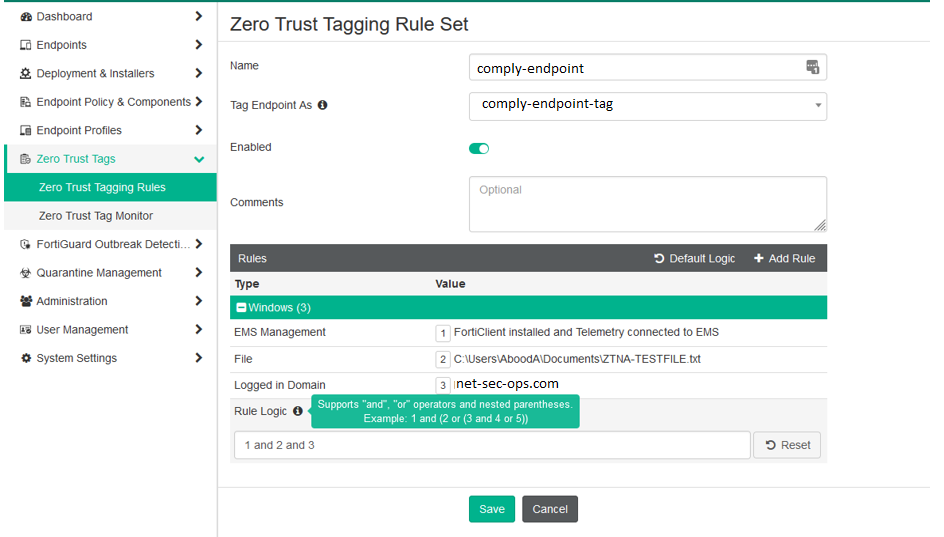
- By default, an endpoint must meet all conditions to satisfy a rule. However, using the “NOT” operator (where supported) or modifying the rule logic allows flexibility—e.g., an endpoint can match condition (1 AND 2) OR 3 instead.
- The screenshot below illustrates this logic in action:
Tag Logic Example
For our Proof of Concept (PoC), we’ve configured two tagging rules in EMS:
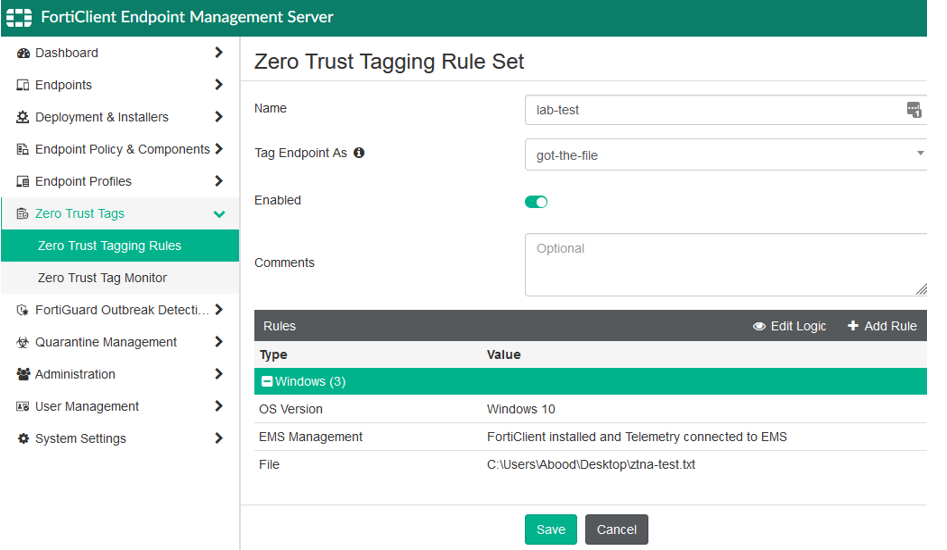
Rule 1: “lab-test”
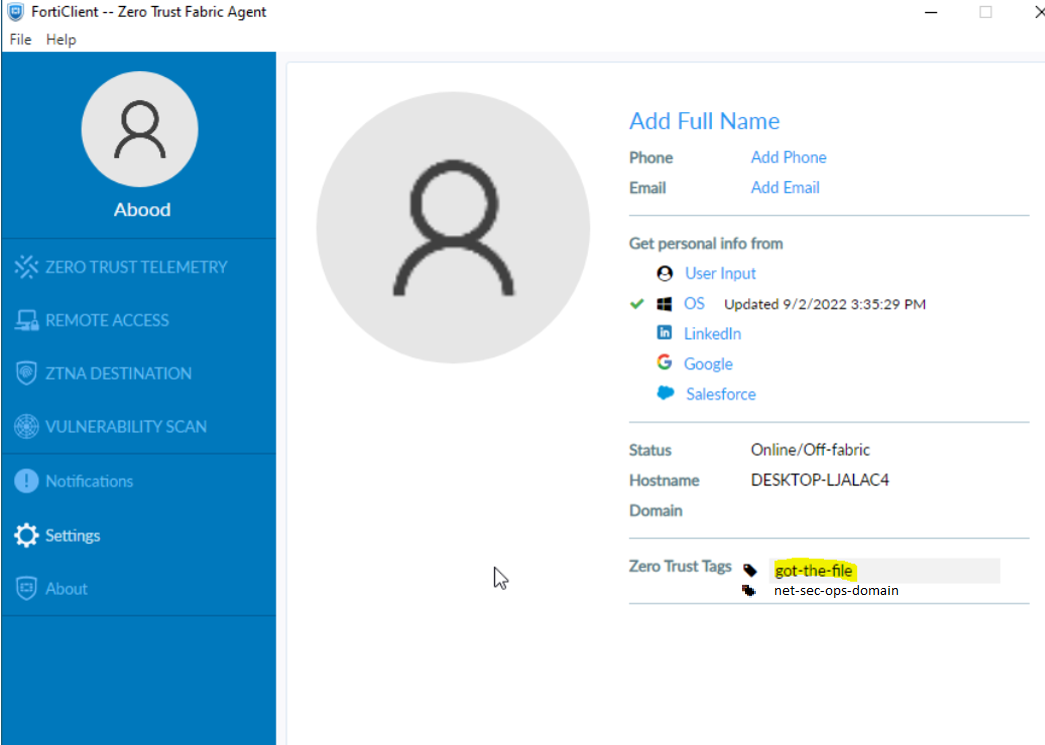
- Tag Name: got-the-file
- Logic: The endpoint must satisfy all conditions to be tagged as got-the-file.
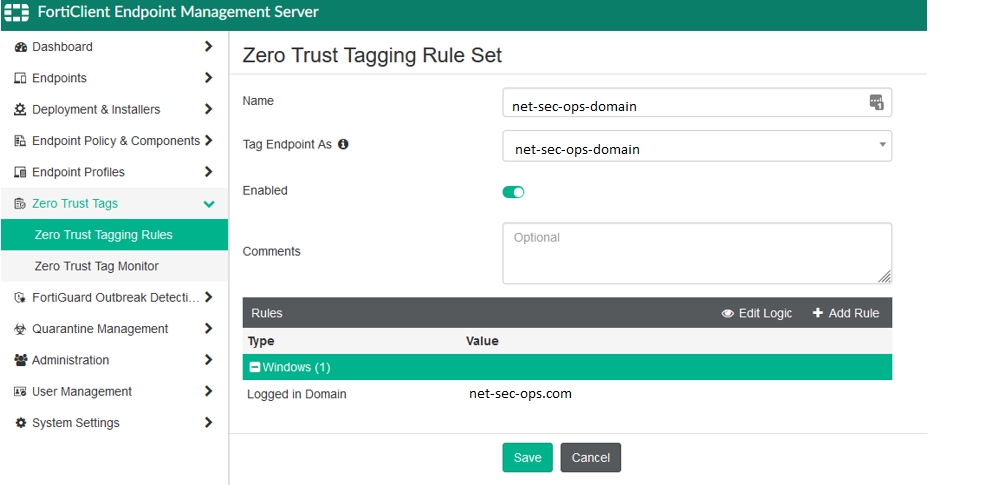
Rule 2: “net-sec-ops-domain”
- Tag Name: net-sec-ops-domain
- Logic: The endpoint must be logged into the net-sec-ops.com.au domain. If this condition is met, the endpoint is tagged as net-sec-ops-domain.
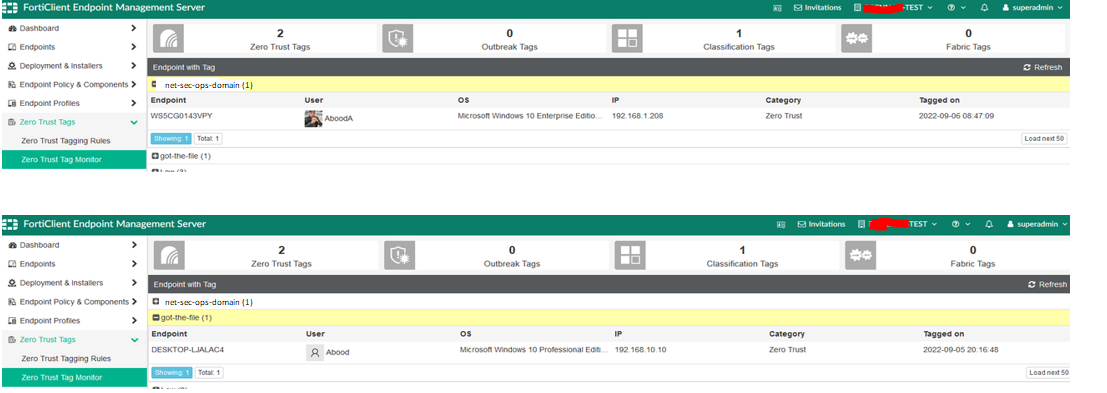
Zero Trust Tag Monitor
The Zero Trust Tag Monitor provides a real-time view of dynamically assigned endpoint tags based on configured rules. If an endpoint connected to EMS meets the rule conditions, the corresponding tags appear in the monitor.
Additionally, you can verify assigned tags directly on the FortiClient:
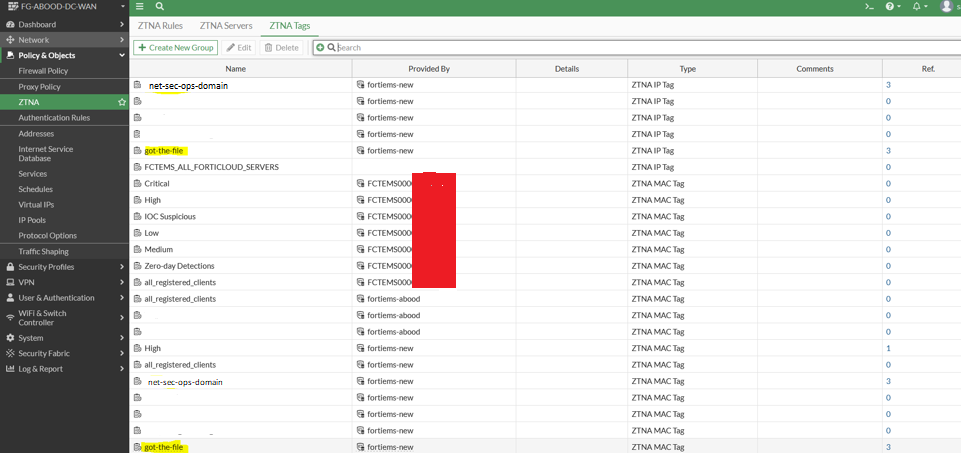
ZTNA Tags in Fortigate
Once the Security Fabric connection between FortiGate and FortiClient EMS is established, all ZTNA tags sync back to FortiGate and are displayed under ZTNA > ZTNA Tags. For this PoC, we focus on two tags:
- net-sec-ops-domain
- got-the-file
Each tag exists in two forms:
- ZTNA IP Tag – Used for full ZTNA (mainly for remote user access).
- ZTNA MAC Tag – Used for on-premises security, controlling access between on-fabric devices, internal web servers, and the internet. (This method does not require an access proxy and can be directly applied to firewall policies.)
Conclusion
ZTNA tags and tagging rules play a crucial role in Fortinet’s Zero Trust security model, ensuring that only compliant endpoints gain access to critical resources. By leveraging FortiClient EMS tagging rules, Zero Trust Tag Monitor, and FortiGate ZTNA tags, organizations can implement a robust access control mechanism for both remote and on-premises users.
Stay tuned for the next part of the Fortinet ZTNA series! 🚀