In the second part of our Fortinet ZTNA series, we explore a practical use case involving remote access to basic on-premises data center resources.
The following high-level diagram illustrates the setup:
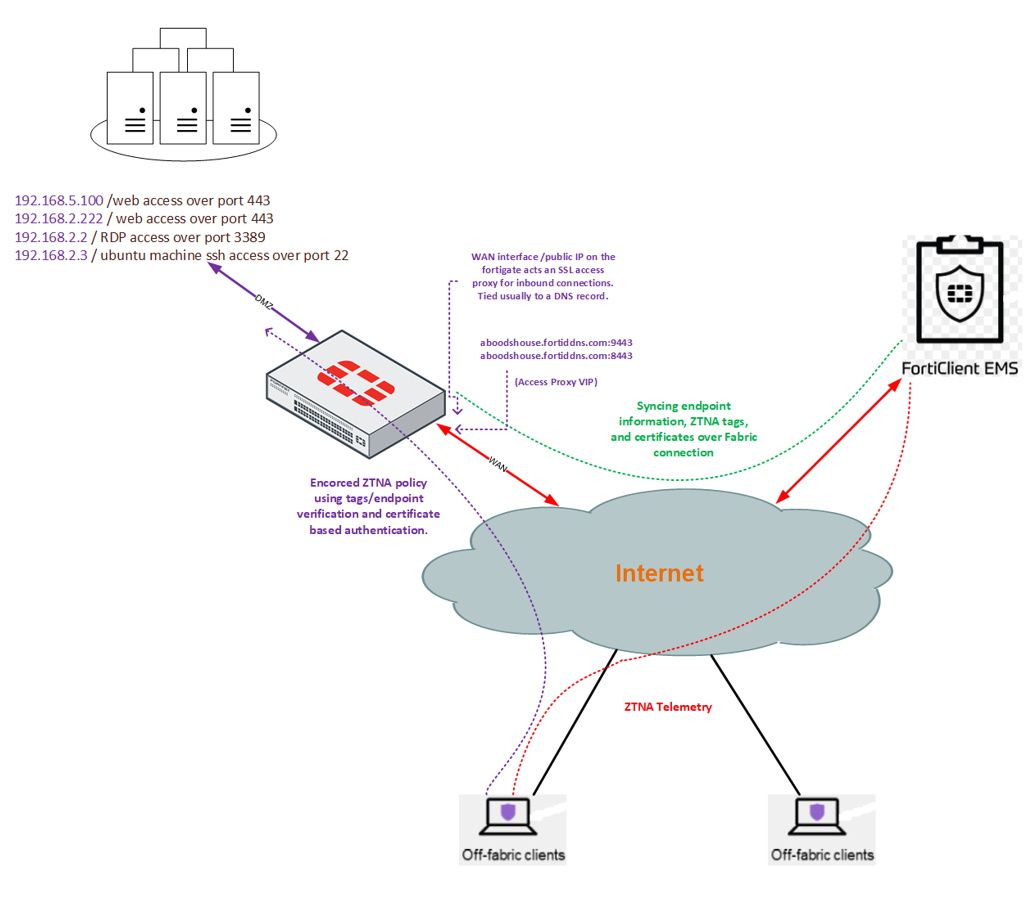
This scenario involves the need for remote access to four servers within the data center, each with different access requirements:
| Server IP | OS | Service | ZTNA Server Access Proxy Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.5.100 | web server over linux | Web access over TCP/443 | HTTPS Access Proxy |
| 192.168.2.222 | web server over esxi host | Web access over TCP/443 | HTTPS Access Proxy |
| 192.168.2.2 | Windows server | RDP access over TCP/3389 | TCP Forwarding Access Proxy |
| 192.168.2.3 | Ubuntu | SSH access over TCP/22 | SSH Access Proxy |
The configuration steps will involve both the FortiGate and FortiClient EMS devices. The following topics will be covered:
- Fortigate & FortiClient EMS connectivity.
- Forticlient & FortiClient EMS connectivity.
- SAML Authentication with Azure as IdP and Fortigate as SP.
- ZTNA access proxy server types, use cases and their basic configuration.
- ZTNA certificate Management.
- ZTNA Destinations configuration.
- ZTNA Rules configuration.
- ZTNA Tags configuration.
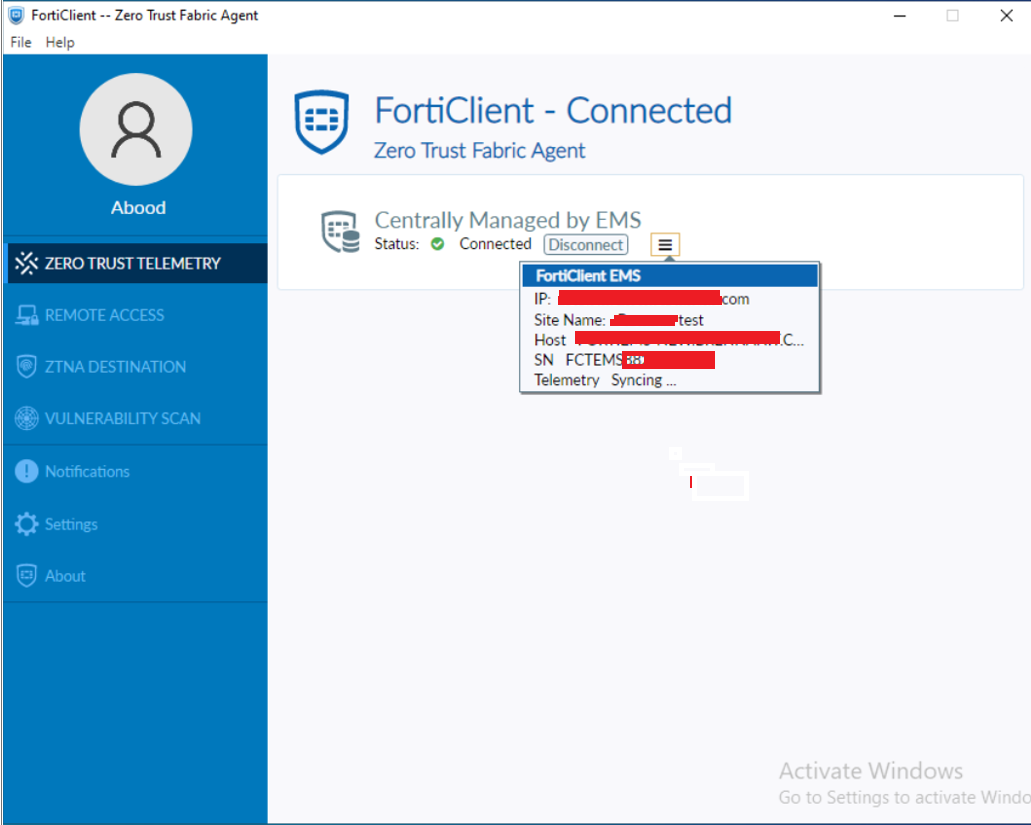
This part focuses on the connectivity between FortiGate/FortiClient EMS and FortiClient/FortiClient EMS.
FortiGate maintains a continuous connection to the EMS server, synchronizing endpoint information and ZTNA tags. This fabric connection plays a critical role in the solution’s functionality and traffic flow.
Fortigate & EMS Connectivity
- FortiGate uses the FortiClient EMS fabric connector to establish a connection with FortiClient EMS.
- For the fabric connection to work, FortiGate must verify the FortiClient EMS server’s certificate. A CA certificate needs to be installed on FortiGate; otherwise, the certificate will not be trusted, causing the fabric connection to fail.
- FortiClient EMS must authorize FortiGate as a fabric device.
Configuration
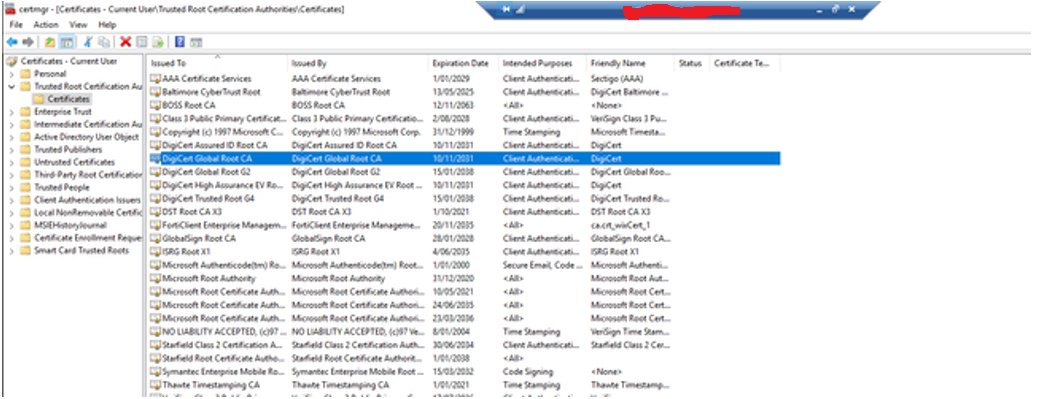
- Export the FortiClient EMS SSL certificate and import it into FortiGate. The certificate is stored in the “Trusted Root Certification Authorities” folder on the FortiClient EMS server. A wildcard certificate can be used, imported as a remote certificate CA in FortiGate.
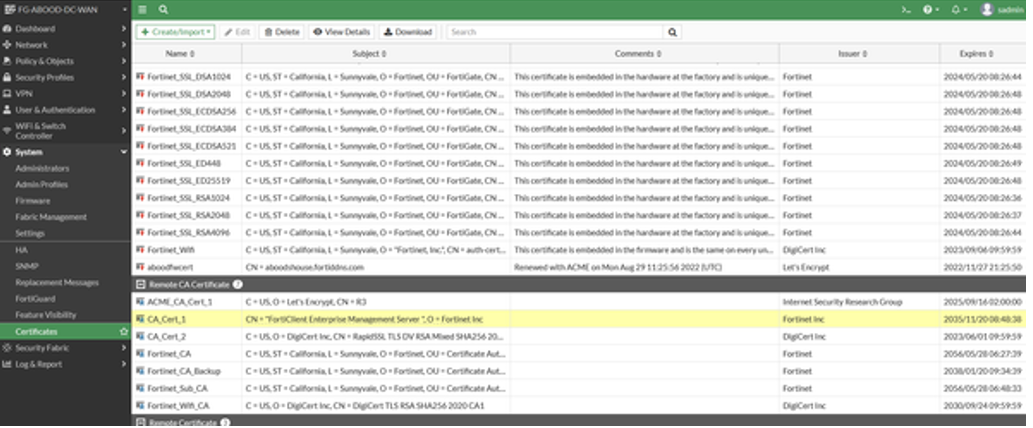
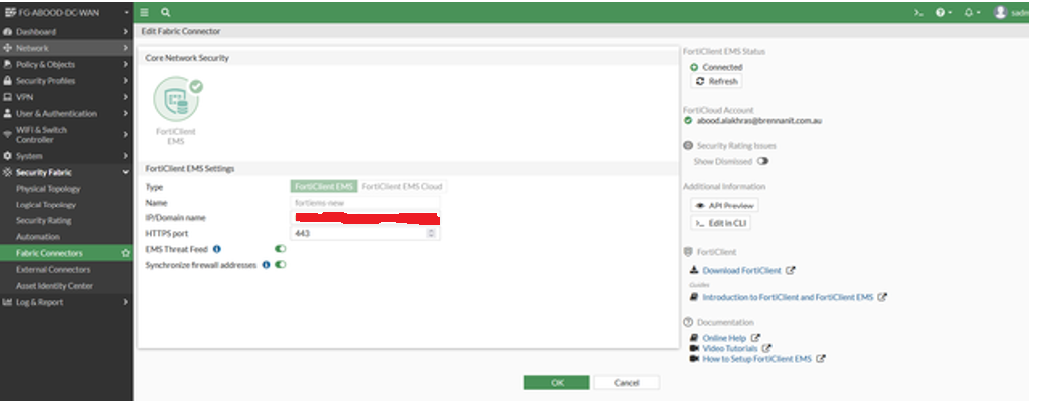
- Add EMS as a fabric device on FortiGate. FortiClient EMS must authorize FortiGate as a fabric device. The fabric connection can connect directly to an EMS server or an EMS tenant. Each customer site/tenant in EMS must have a DNS A record pointing to FortiEMS for the fabric connection.
After logging into FortiClient EMS, a pop-up will prompt you to authorize FortiGate. Until authorized, the FortiClient EMS connector status will show “down.”
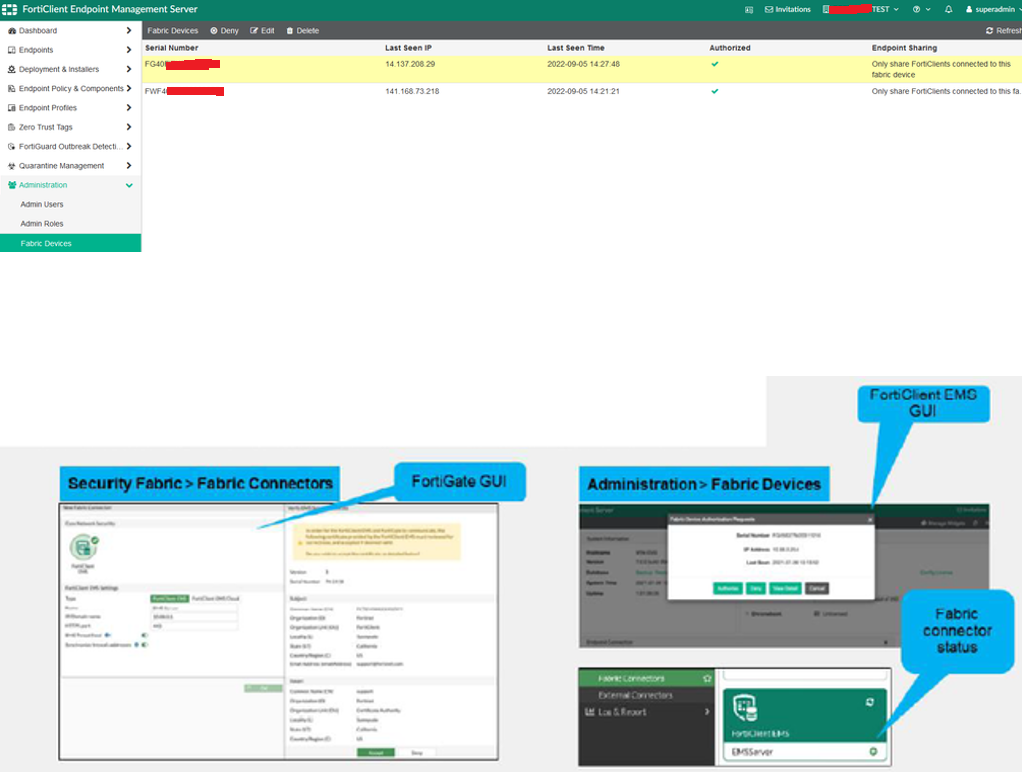
Under Administration → Fabric Devices, you will see the FortiGate authorized as a fabric device.
Once connected, FortiGate will automatically synchronize ZTNA tags from FortiClient EMS.
Forticlient & FortiClient EMS Connectivity
- The FortiClient endpoint must establish a connection to FortiClient EMS.
- The telemetry connection between FortiClient and FortiClient EMS is a crucial dependency of the ZTNA solution. This step must be completed before moving on to further configurations (with the first step being the fabric connection between FortiGate and FortiClient EMS).
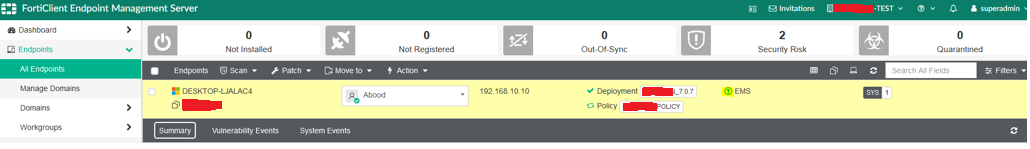
- The connection can be verified on the FortiClient console under the Zero Trust Telemetry menu or by navigating to Endpoints > All Endpoints in FortiClient EMS.
- FortiClient EMS listens for incoming connections from FortiClients on TCP/8013, so ensure inbound access to this port is allowed on the public network.